How to Find the Best Air Compressor Supplier in China
Choosing the right air co…
Read More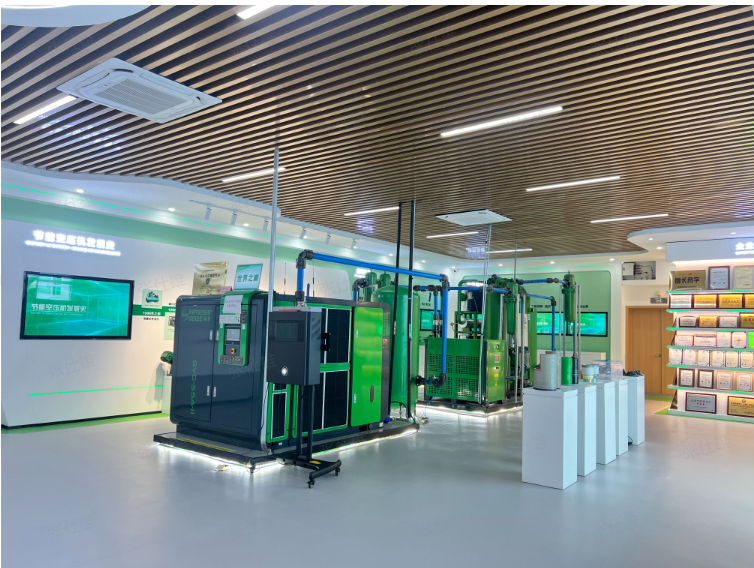






Cumulative sales
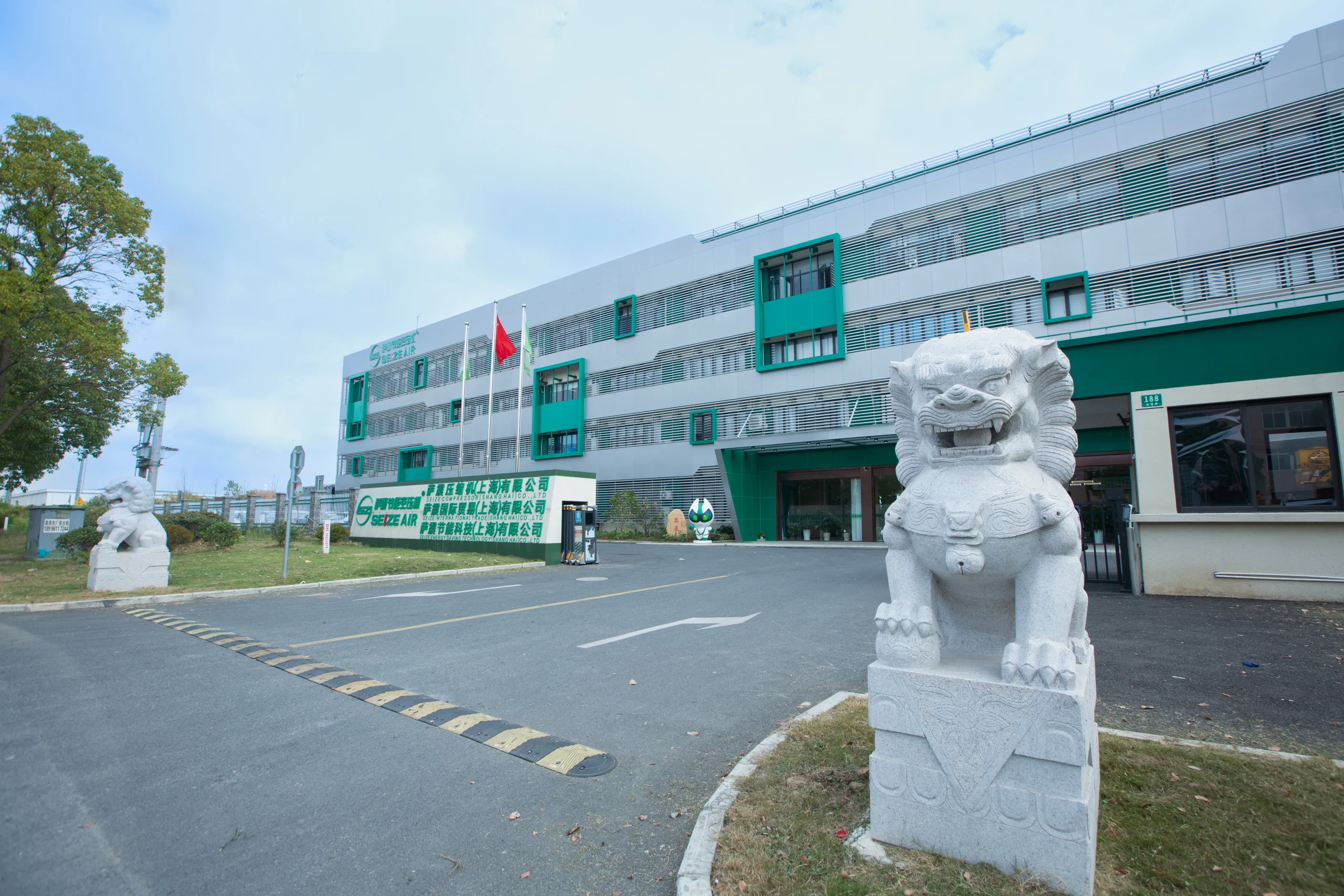
SEIZE COMPRESSOR (SHANGHAI) CO., LTD
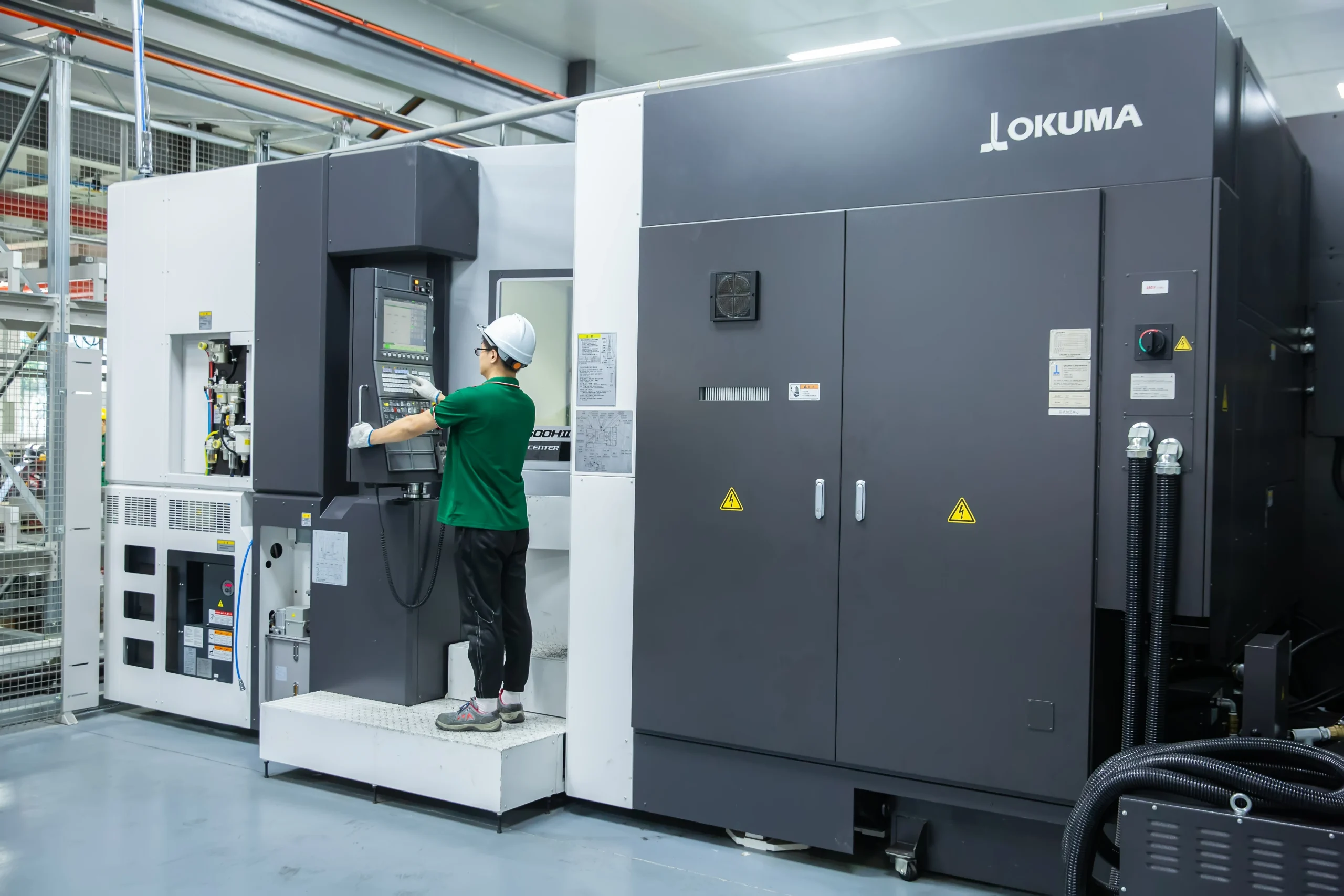
Seize Air is a global pioneer in energy-efficient air compressors! The company integrates R&D, manufacturing, marketing and servicing, and specialises in producing energy-efficient air compressors.
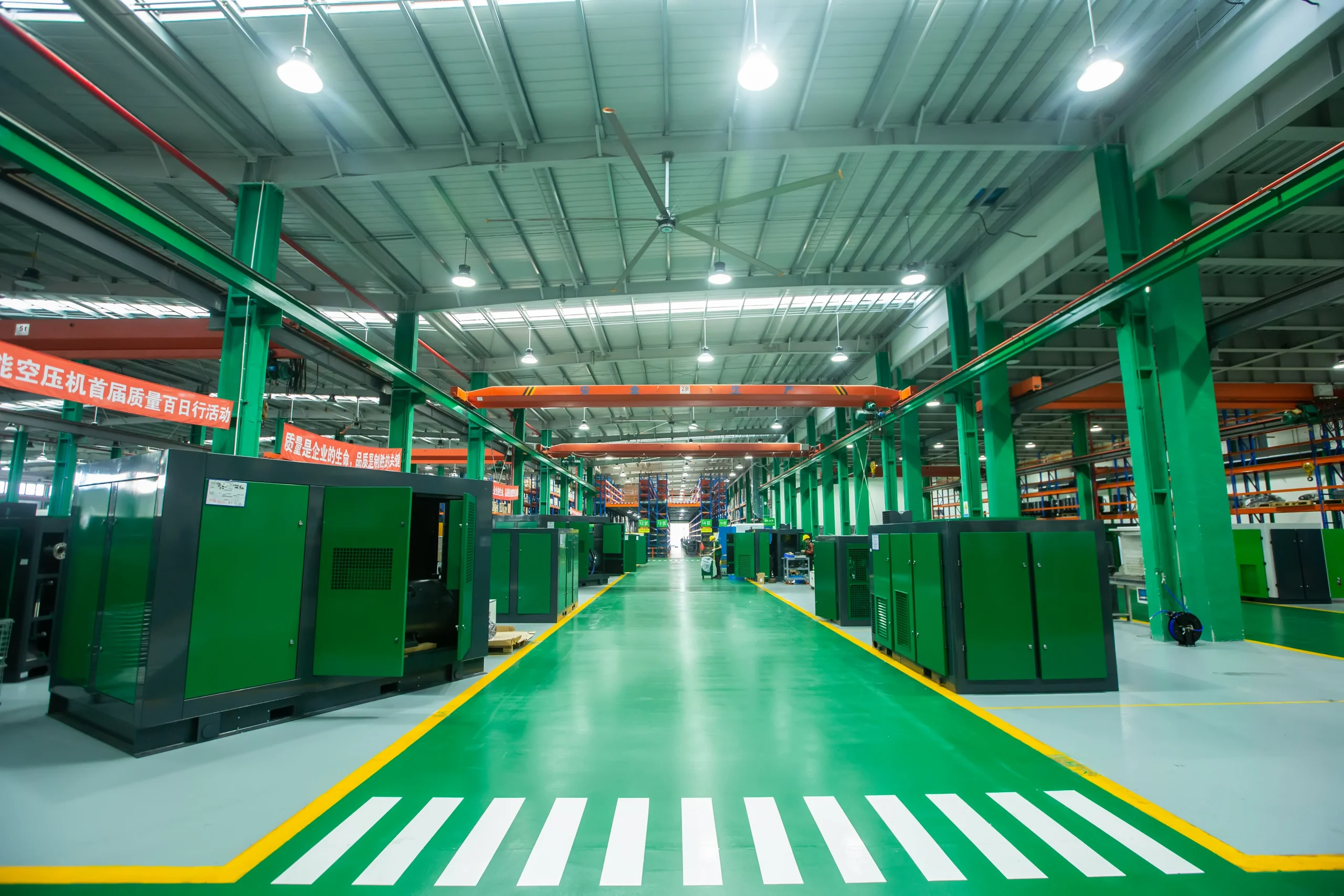
We employ over 400 staffs and have more than 200 sales and service outlets at home and abroad. We were the first large-scale manufacturer to replace imported brands. To date, we have sold over 30,000 energy-efficient air compressors worldwide, with cumulative sales exceeding 3 million kW. SEIZE AIR has saved our customers a total of 2.5 billion USD in electricity costs and reduced carbon emissions by around 15 million tonnes.

Have A Question
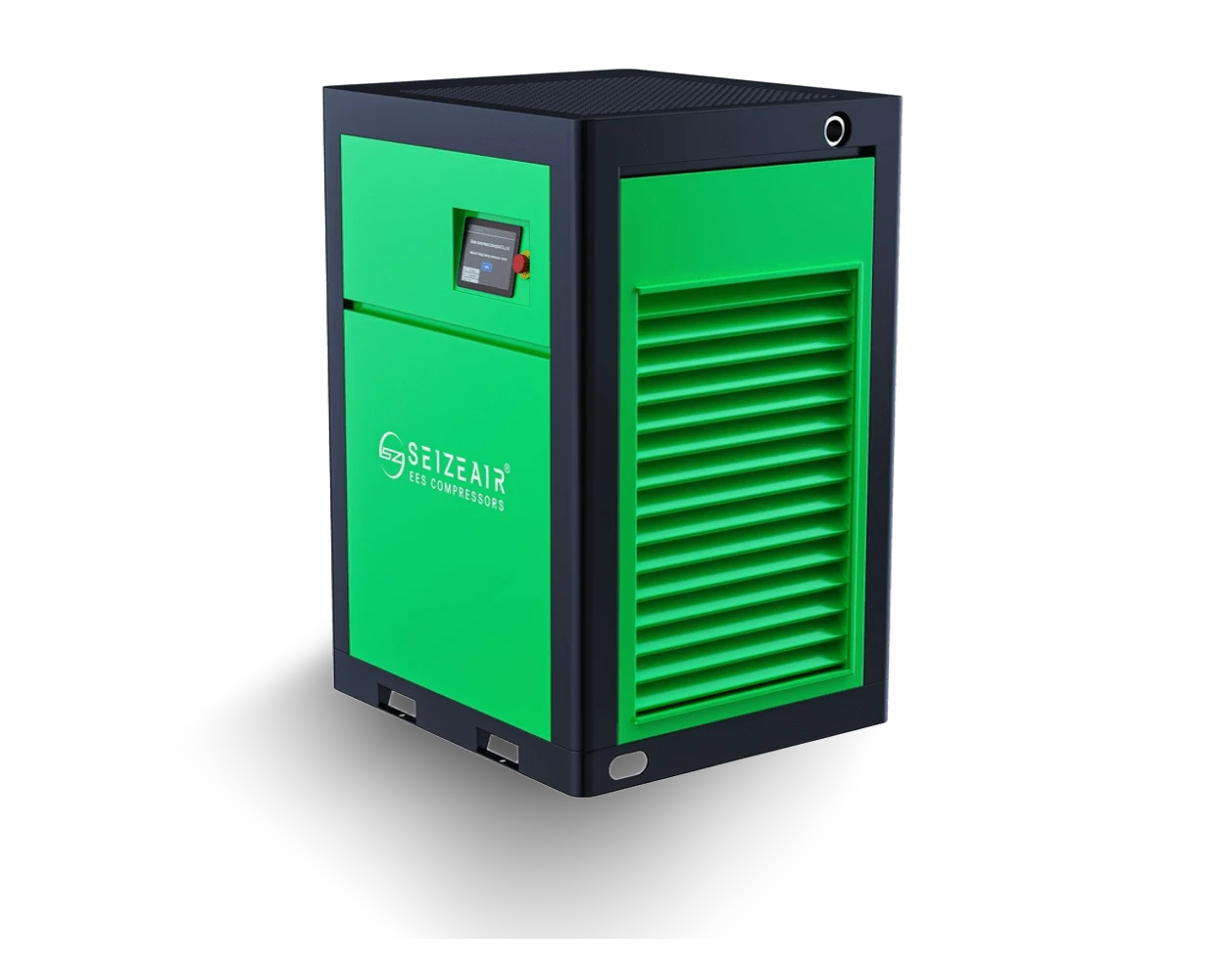
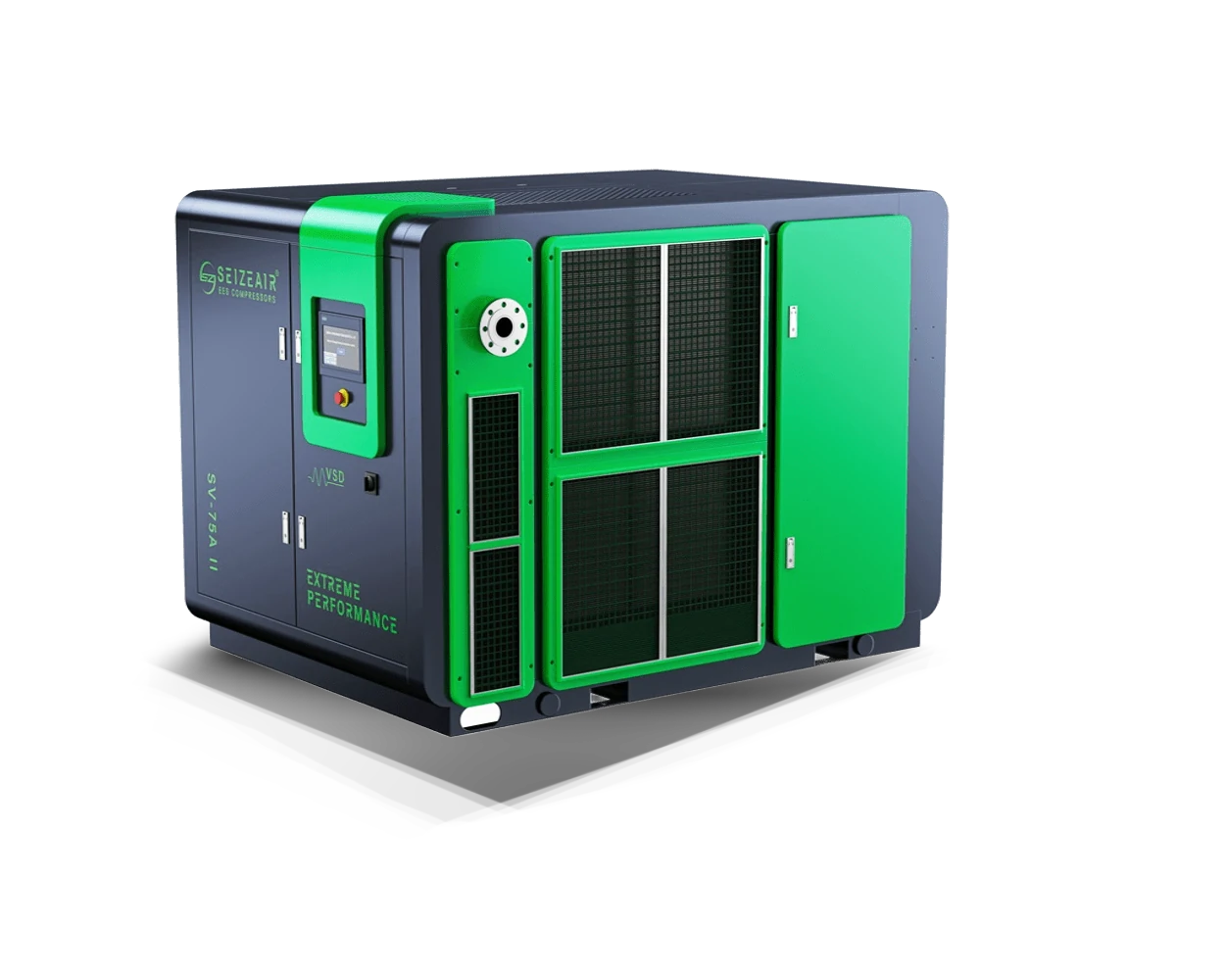
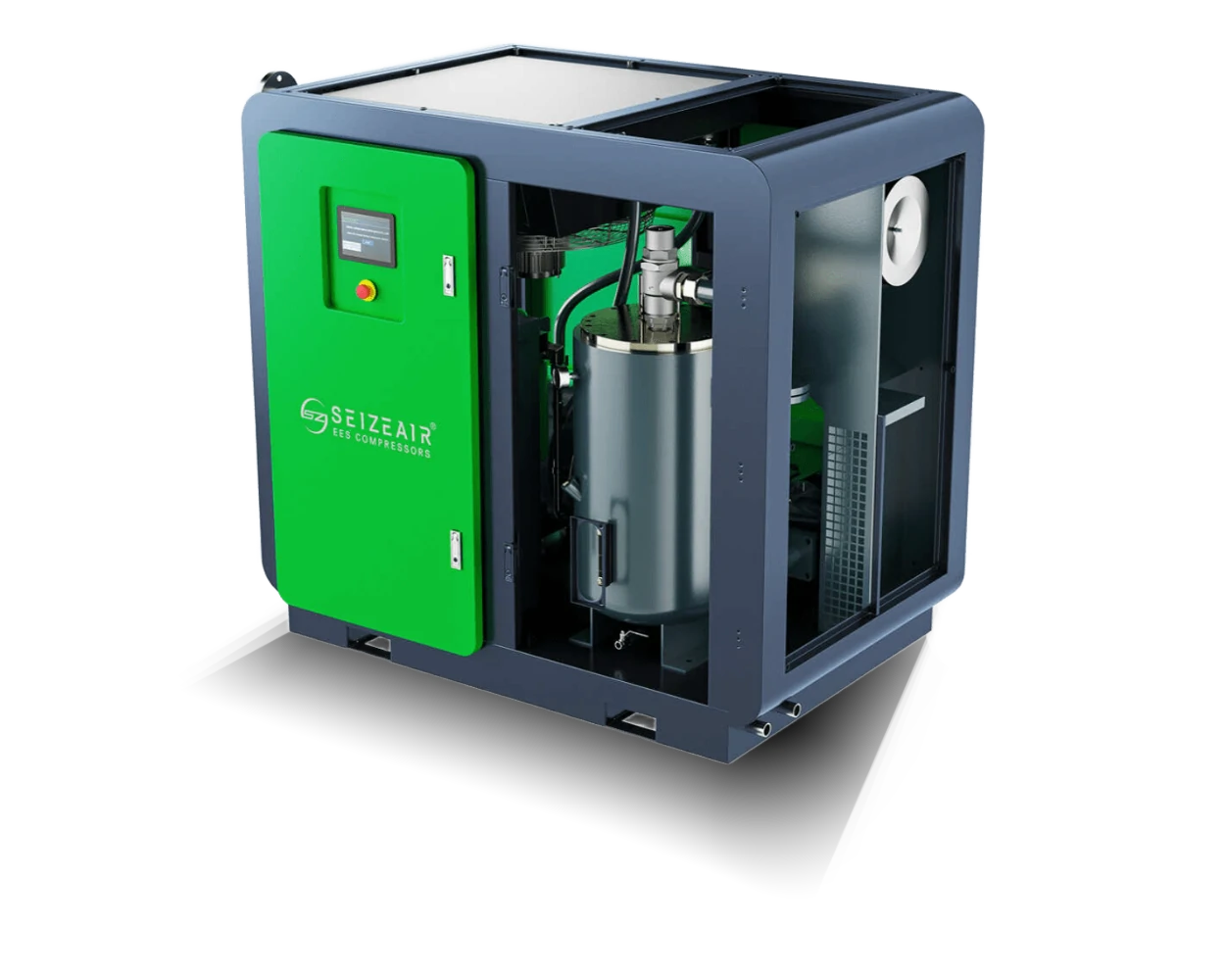
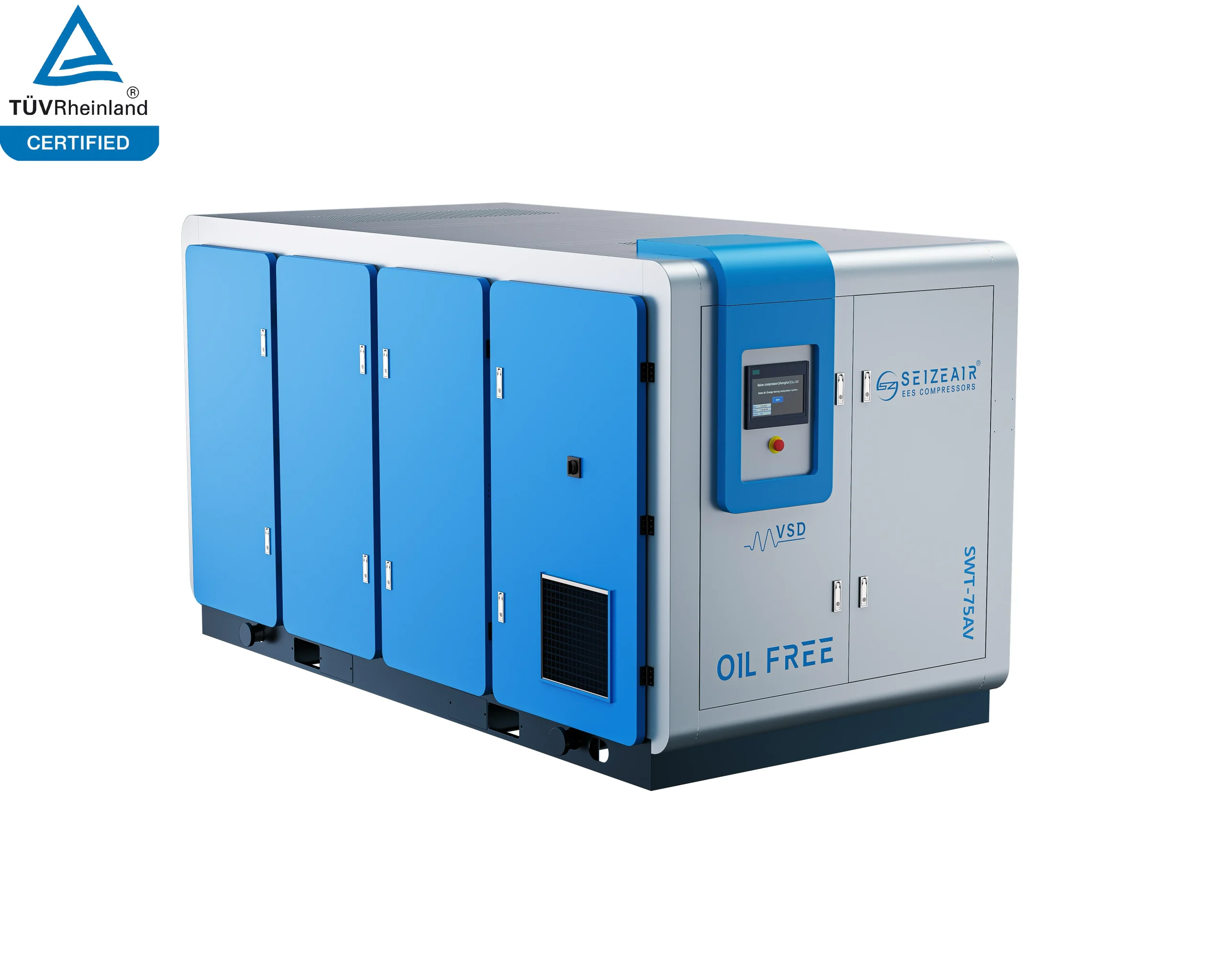




SEIZE AIR: the pioneer of global energy-saving air compressor
With independent core technology, energy-saving air compressor dual invention patents! The company integrates R&D, manufacturing, marketing and service, and is a brand manufacturer focusing on energy-saving air compressors!
Contact us now to inquire about our policy!
101+ patented technologies that have received international recognition
Services in more than 200 countries and regions
Plant area
Cumulative numberof sold units
Global Customers
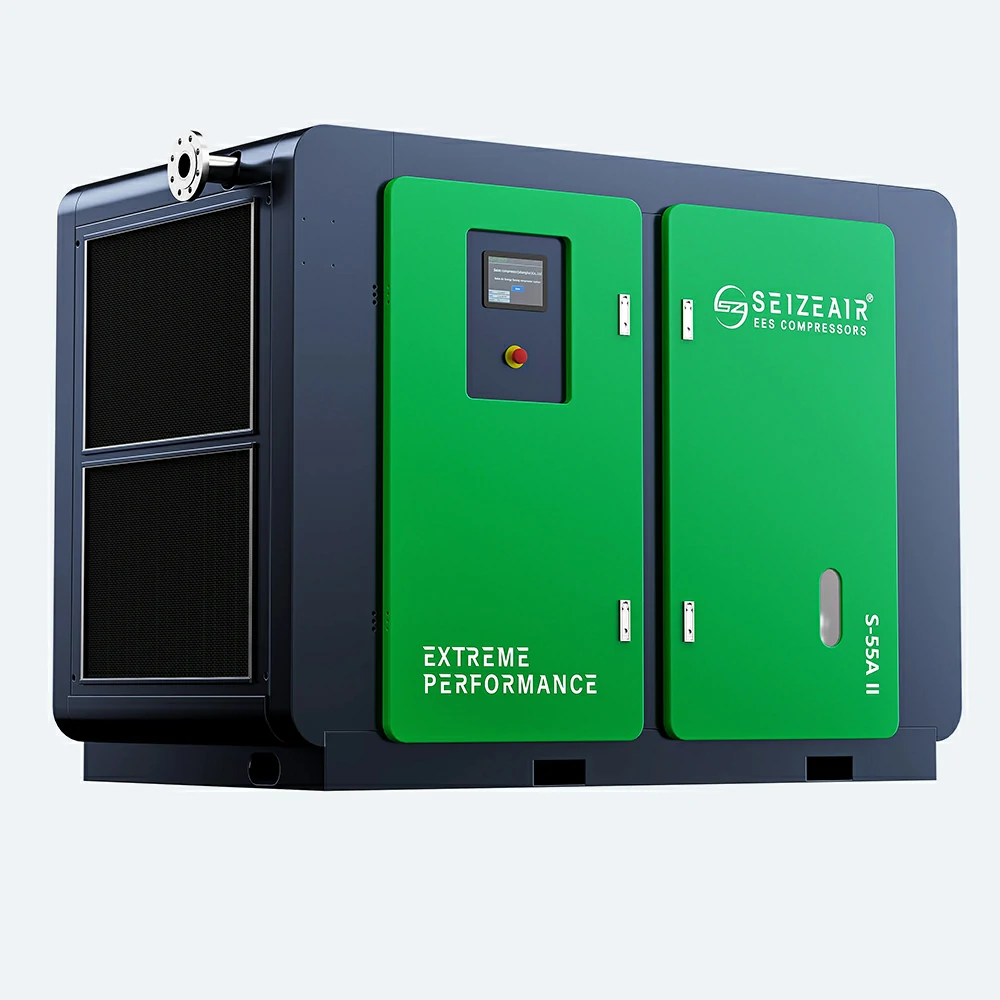
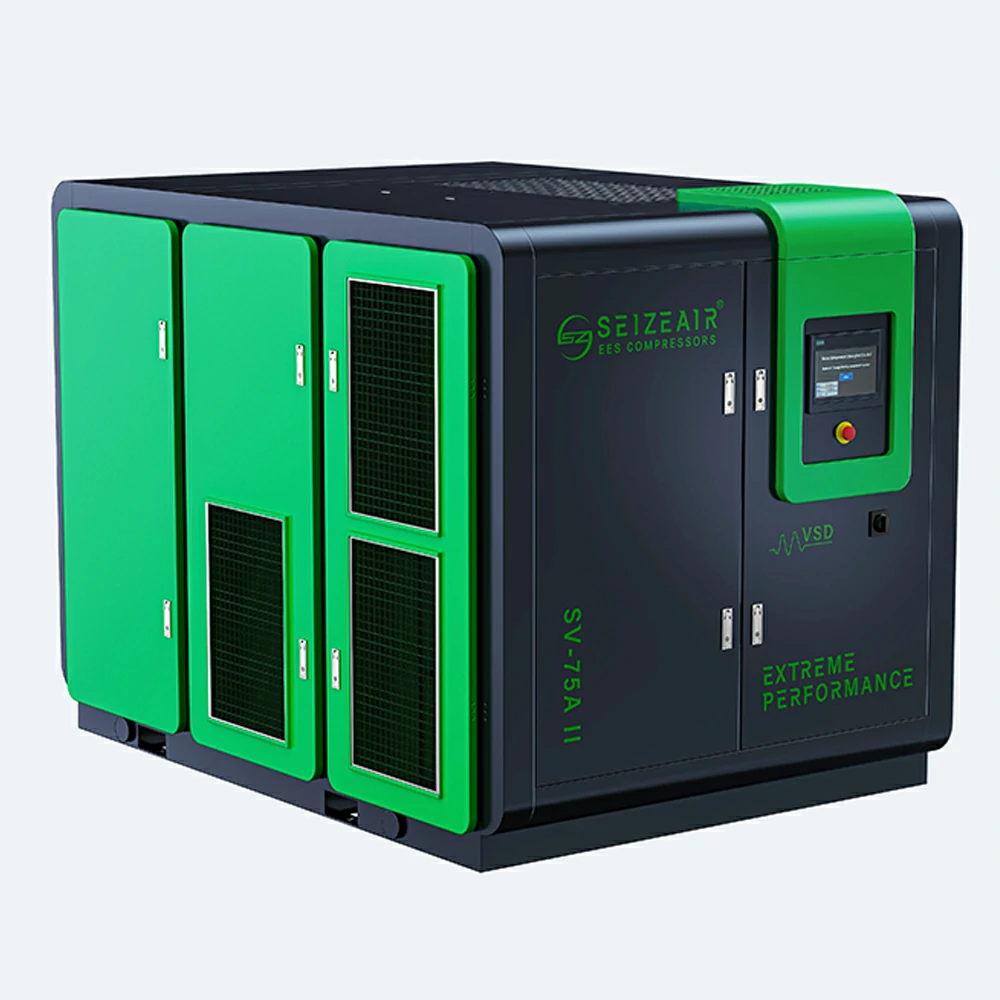
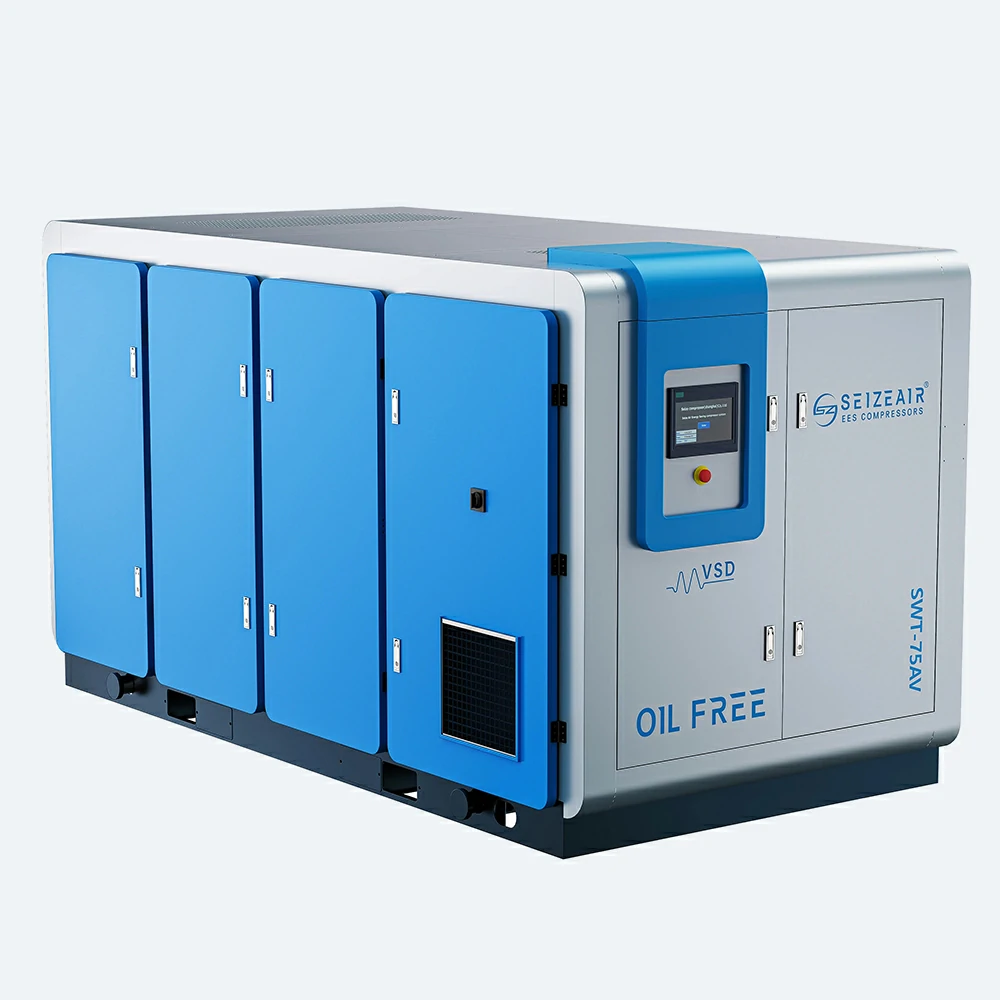
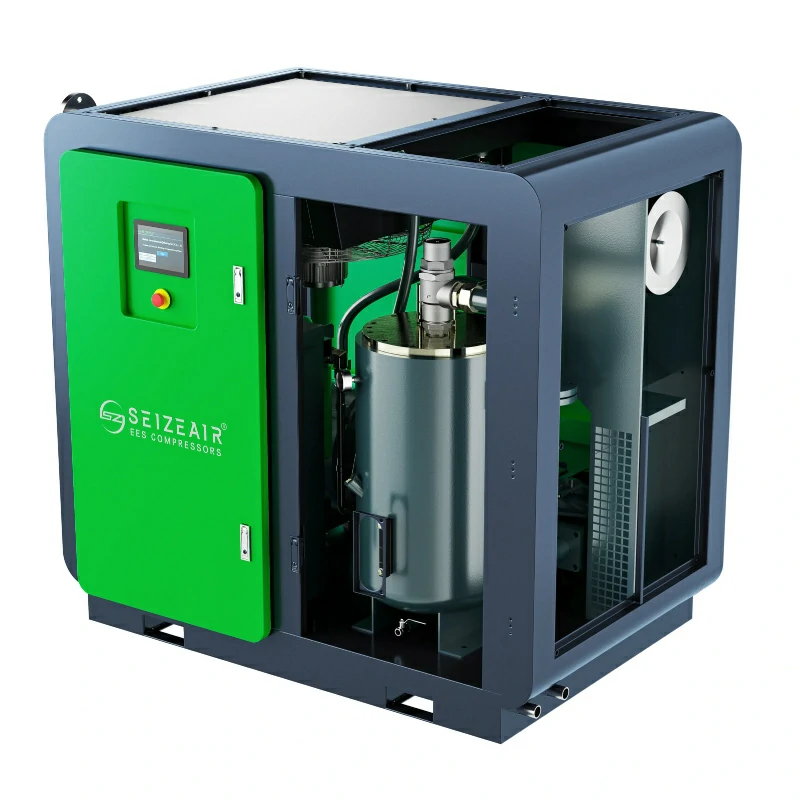
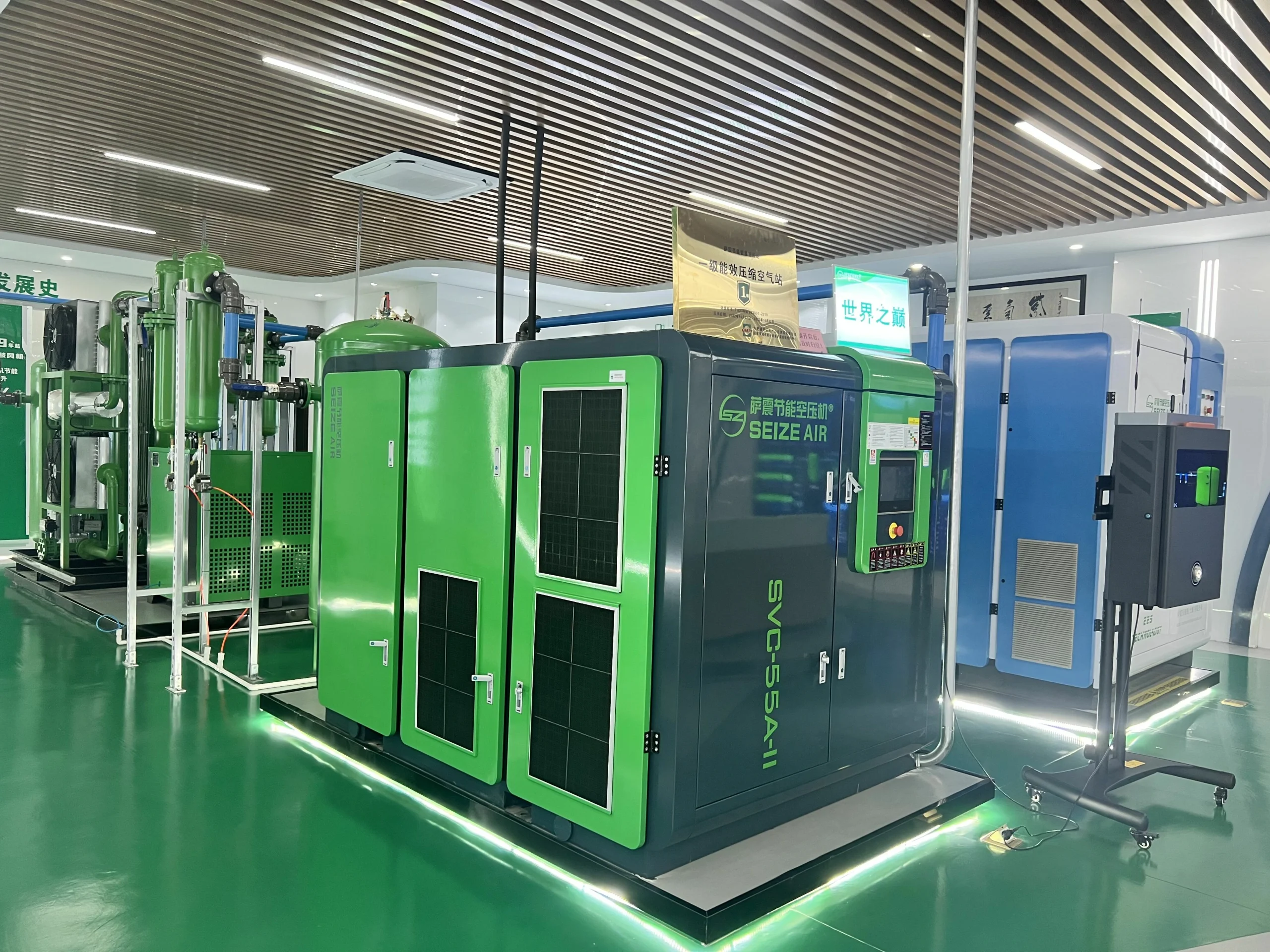
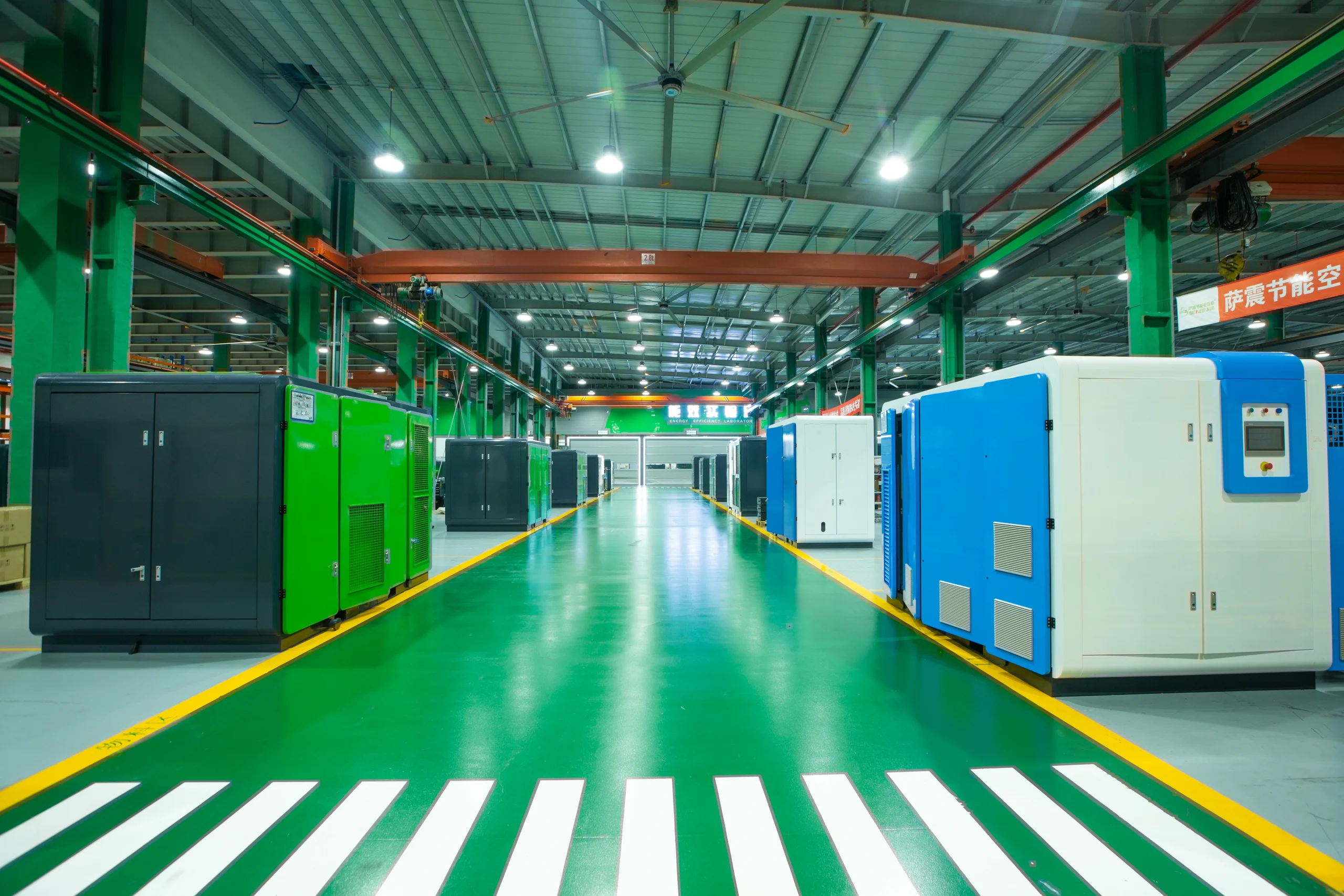
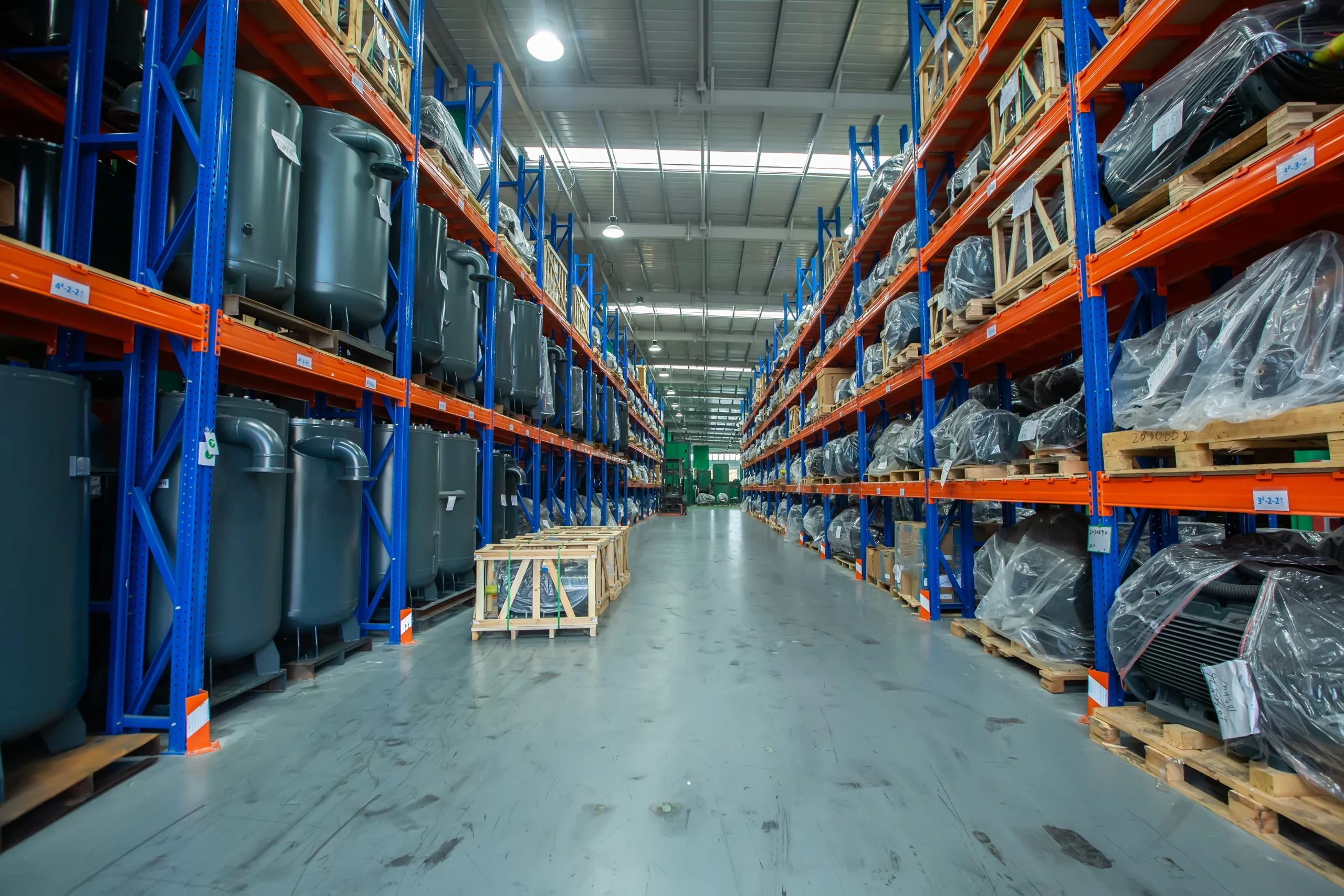
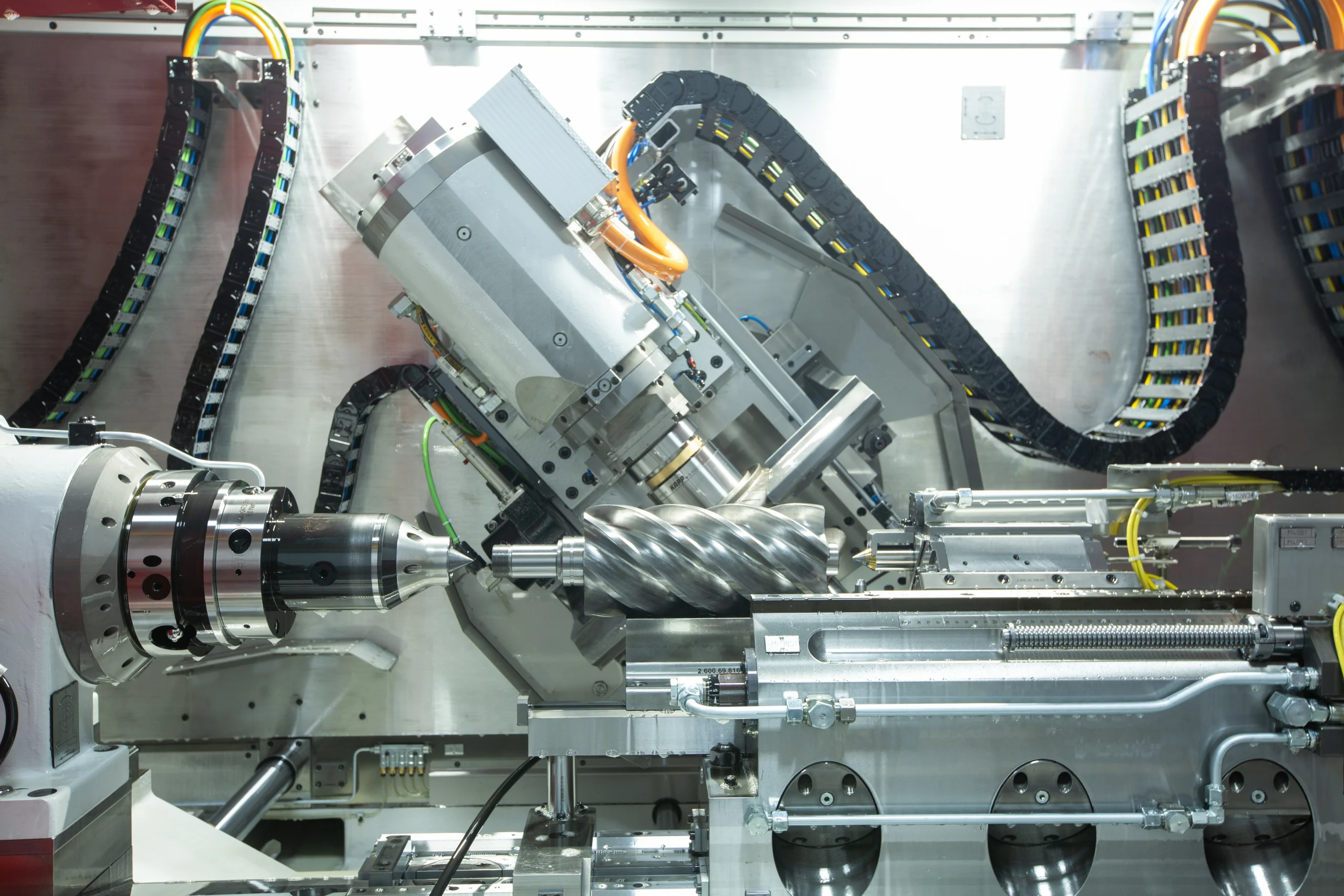
Seize is a professional air compressor manufacturer, we provide permanent magnet variable speed air compressor screw air compressor, oil free air compressor, portable compressor, high pressure air compressor, low pressure series air compressor,centrifugal air compressor,etc.
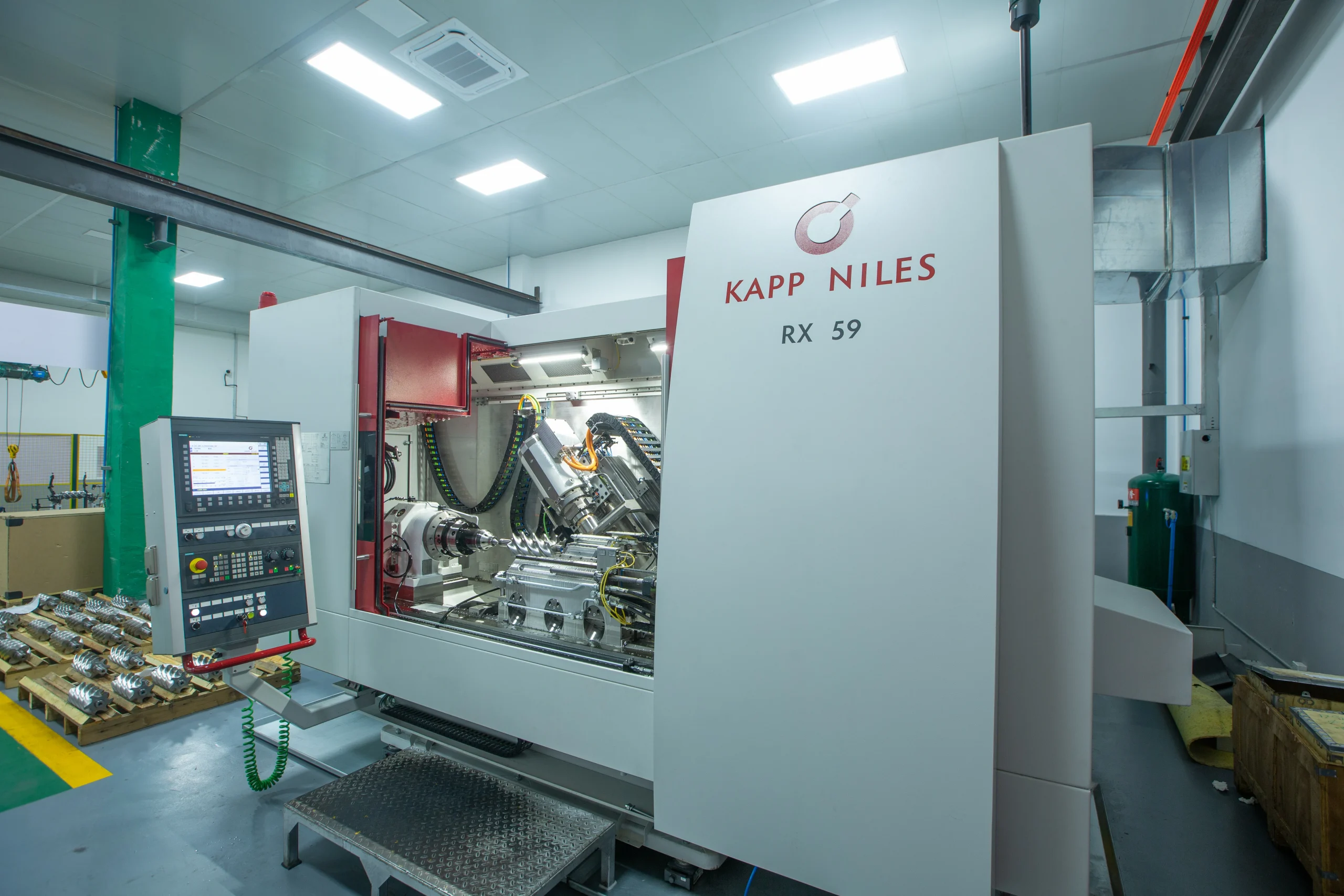
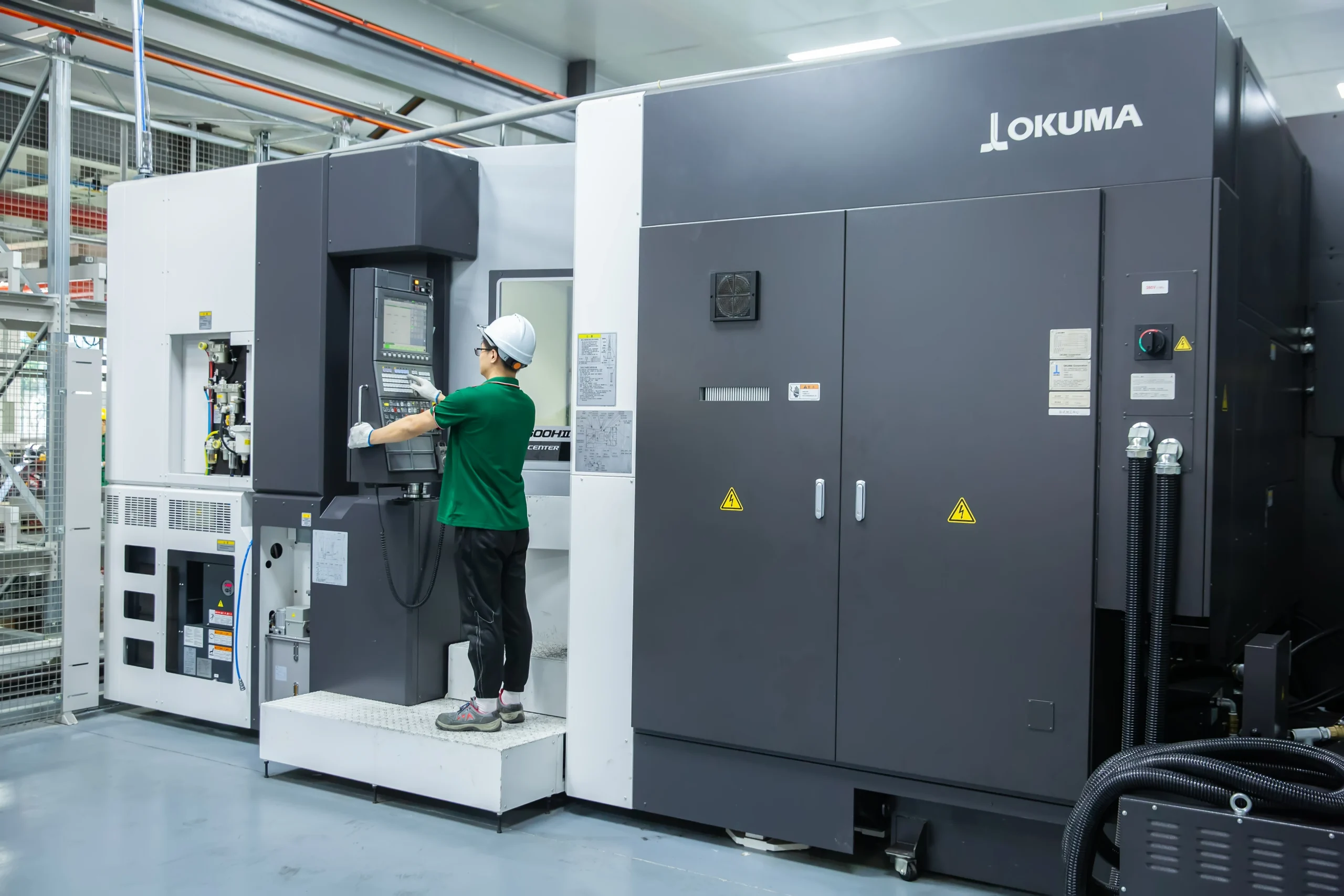
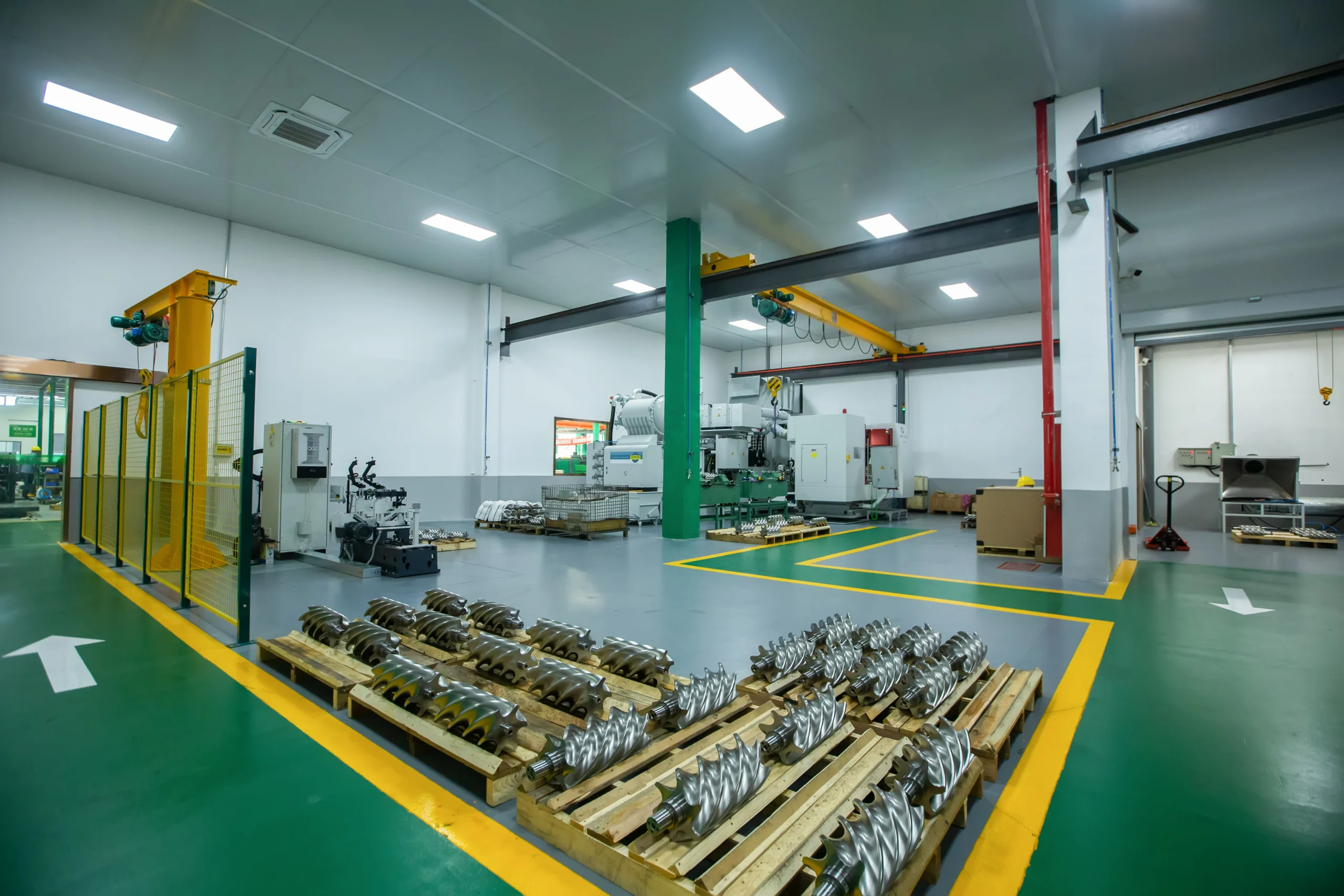
At present,our manufacturing base is in Shanghai, China and we have more than 30 service points overseas which can provide users with professional sales and service support in time.



















































Choosing the right air co…
Read MoreIn the food industry, pro…
Read MoreIn the pharmaceutical ind…
Read MoreStrengthening Products, E…
Read More