Introduction: Traditional vs. Energy-Efficient Air Compressors
Traditional compressors suffer from pressure swings, while VSD compressors use PID control for stable operation, saving 7% energy per 0.1MPa reduction.
This article compares design principles, energy-saving technologies, and real-world case studies to demonstrate the advantages of modern oil-injected screw compressors over conventional models.
1. Key Differences: Traditional vs. Energy-Efficient Air Compressors
| Feature | Traditional Fixed-Speed Compressor | Energy-Efficient Oil-Injected Screw Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Constant speed, frequent starts/stops | Variable speed drive (VSD), on-demand air supply |
| Efficiency | Low (high specific power input) | High (IE4 motor + two-stage compression) |
| Pressure Control | High pressure fluctuations, “unloading” losses | Constant pressure (±0.01MPa), no wasted energy |
| Idle Power | Consumes 40%-50% of full-load power | Near-zero idle consumption with VSD |
| Maintenance | High wear, frequent servicing | Smart controls extend component lifespan |
2. How Oil-Injected Screw Compressors Save Energy
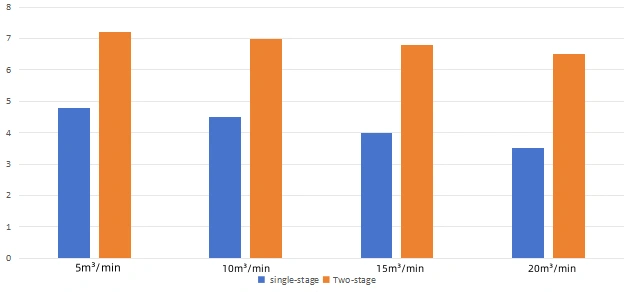
(1) Two-Stage Compression Technology
Traditional single-stage compressors lose efficiency at high pressure ratios. Two-stage compression uses dual rotors to reduce compression ratio per stage, minimizing internal leakage and heat loss.
✅ Energy Savings: 12%-17% higher efficiency vs. single-stage compression.
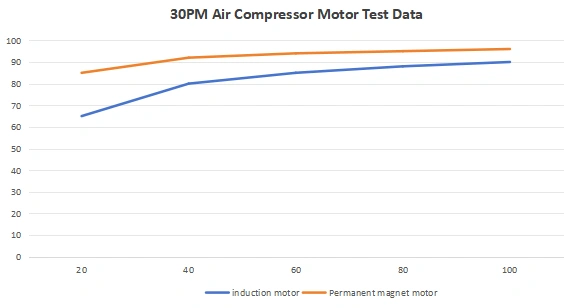
(2) Permanent Magnet Motor (IE4/IE5)
Standard induction motors are only 87%-89% efficient, while permanent magnet (PM) motors reach 94%-97% efficiency with adjustable speed to match demand.
✅ Energy Savings: 20%-30% lower power consumption, especially at partial loads.
(3) Intelligent Pressure Control
Traditional compressors cycle between “load” and “unload,” causing pressure swings. VSD compressors use PID control to maintain stable pressure (±0.01MPa), eliminating over-compression.
✅ Energy Savings: Every 0.1MPa pressure reduction saves 7% in energy.
| Pressure Control Method | Pressure Fluctuation Range (MPa) | Energy Consumption (Relative Value) | Energy Savings Ratio |
| Traditional compressors | ±0.2 | 100% | 0% |
| VSD | ±0.01 | 93% | 7% |
(4) Advanced Cooling & Heat Recovery
Traditional compressors suffer from overheating, reducing performance. Energy-efficient models use oversized coolers + VSD fans to maintain optimal oil temperature (80-85°C), with optional heat recovery for heating/water.
✅ Energy Savings: Heat recovery systems reclaim 60% of waste heat.
3. Case Studies: Proven Energy Savings
Case 1: Cement Plant 132kW Compressor Upgrade
| Metric | Traditional Fixed-Speed | Seize PM VSD Two-Stage | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Power Use | 1,166,000 kWh | 820,000 kWh | 346,000 kWh/year |
| Electricity Cost (¥0.65/kWh) | ¥758,000 | ¥533,000 | ¥225,000/year |
| Payback Period | — | 14 months | — |
✅ Energy Reduction: 29.6%
Case 2: Textile Factory 75kW Compressor Retrofit
| Metric | Traditional VSD | Seize Two-Stage PM | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Factor | 70% | 95% | Reduced idle losses |
| Annual Cost | ¥480,000 | ¥340,000 | ¥140,000/year |
| Noise Level | 78 dB | 72 dB | Quieter operation |
✅ Energy Reduction: 25%

Conclusion: Lower Operating Costs with Energy-Efficient Compressors
Modern oil-injected screw compressors deliver 20%-40% energy savings through two-stage compression, PM motors, smart controls, and heat recovery, with payback typically within 1-2 years. For energy-intensive industries, upgrading to efficient compressors is both an environmental and economic imperative.
🔧 Need a customized solution? Contact Seize Air experts for a free energy audit!










